Agriculture: What it is and how it develops

Reading time
Content
Agriculture is the essential activity of growing plants and raising animals to produce food, fibre, medicines, flowers and other products for the sustainment of human civilization and energy. Its roots go back to the Neolithic, a time when hunters and gatherers began to settle and domesticate the first plants and animals.
With the Industrial Revolution and the advent of machines in agriculture, the industry was dramatically transformed. Mechanisation, the use of artificial fertilisers and irrigation technology, as well as the breeding of highly productive varieties, have greatly increased efficiency and yields. This trend continues with modern developments such as automation and robotics.
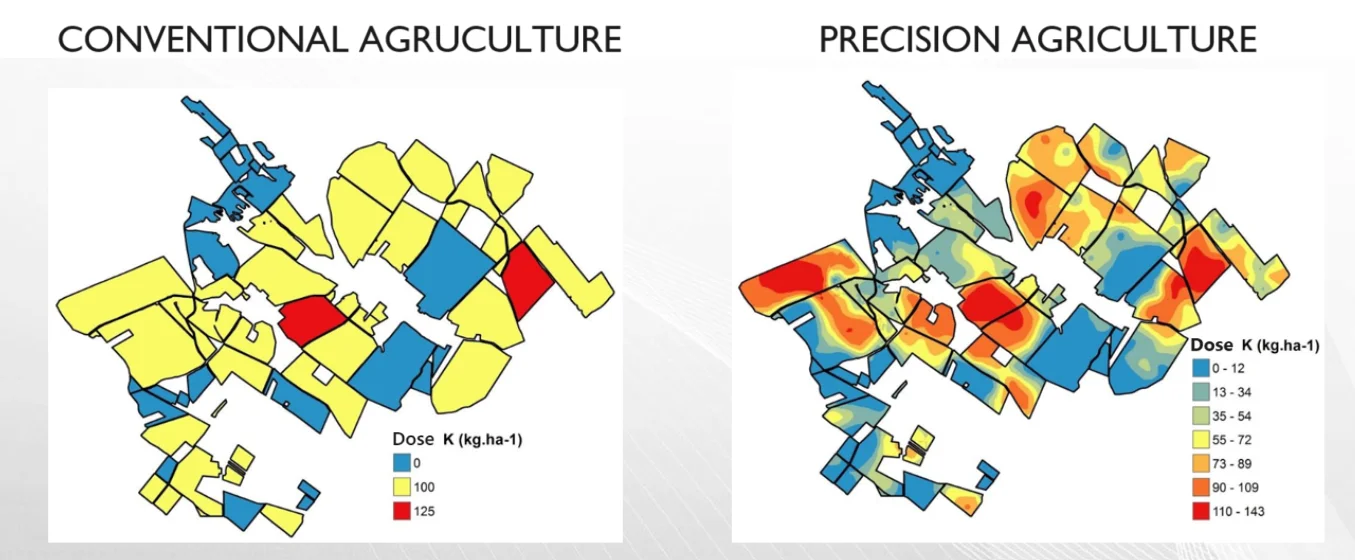
Today's agriculture is increasingly focused on precision, allowing growers and farmers to efficiently manage fields and herds with high accuracy through the use of advanced technologies such as satellite imagery, field sensors, automated vehicles and Big Data. Precision farming is focused on maximizing the yield from each hectare while minimizing the impact on the environment.
One of the main goals of modern agriculture is to ensure food safety - that food is safe and free from harmful substances - and food security, which means that all people have access to sufficient nutritious food at all times. These aspects are crucial for population health and social stability.
Agriculture not only plays a role in the production of food and raw materials, but also has other functions. It supports biodiversity, maintains cultural landscapes, contributes to water cycle and climate regulation and provides opportunities for recreation and tourism.
Modern agriculture stands at a crossroads where technology and tradition go hand in hand to support sustainable growth and population health. The use of genetic engineering and bioengineering can greatly improve crop resilience and yields, while government policies and regulations play a key role in increasing efficiency and protecting public health and the environment.
